Features
A group of Modern Languages students from Oxford University are documenting their time abroad in Brazil via the BBC.
'Para Inglês Ver', or 'For the English to See', is a series of blogs hosted by BBC Brasil that allows the students to share their impressions of the country – from music, arts and culture to race relations and politics – as they travel around during the first few months of 2014.
The blogs are written by Oxford Modern Languages students reading Portuguese combined with another language or other subjects.
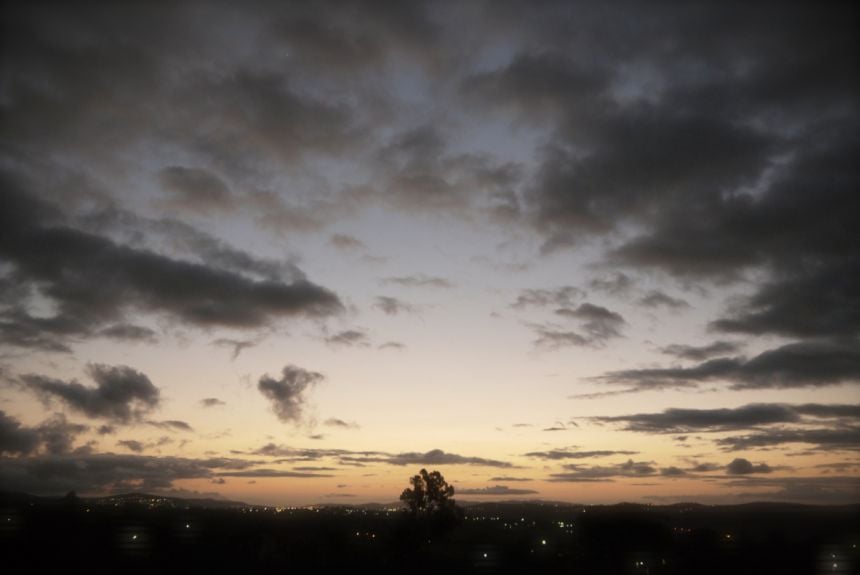 Credit: Lily Green
Credit: Lily GreenShe told Arts at Oxford: 'The project evolved from a series of meetings. I met Juliana Iootty of the BBC during Brazil Week, a cultural event organised by one my tutors, Dr Claire Williams.
'Juliana suggested that some of the Portuguese students should come and visit Broadcasting House, where we were given a tour and talked about potential projects. We then had a second meeting with Silvia Salek of BBC Brasil, who suggested the blog.
'So it was pretty organic, and Juliana and Silvia were both really encouraging and just as enthusiastic about the project as we were.'
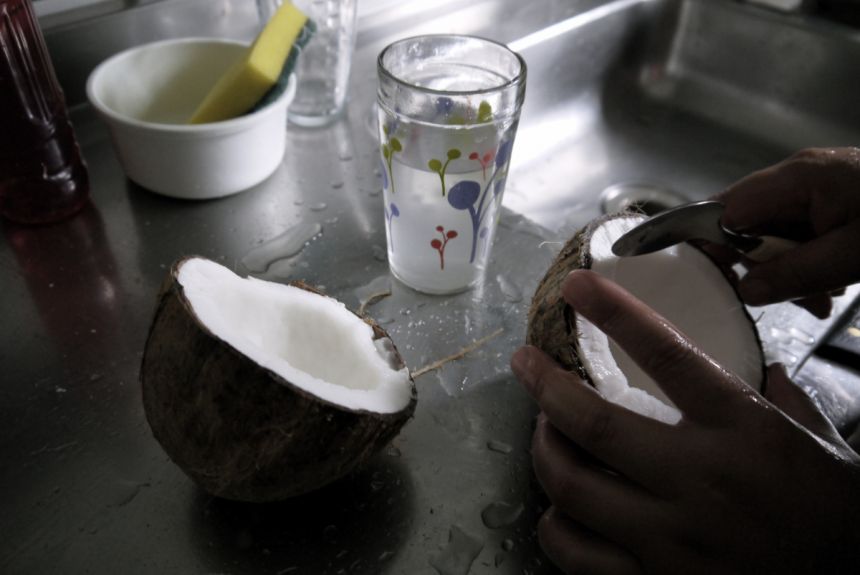 Credit: Lily Green
Credit: Lily GreenShe said: 'From living with a host family and talking to them, as well as colleagues and friends, I know that the things I've written about will get a debate going among Brazilian people. They're the kinds of topics that come up on the commute to work, or in the staff room, or round the dining table.
'The writing process has been difficult, as there is so much I want to say, with so many subtleties. Writing about social issues for social media is a world away from our 2000-word essays. But it has been great to step out of the books and into the real world.'
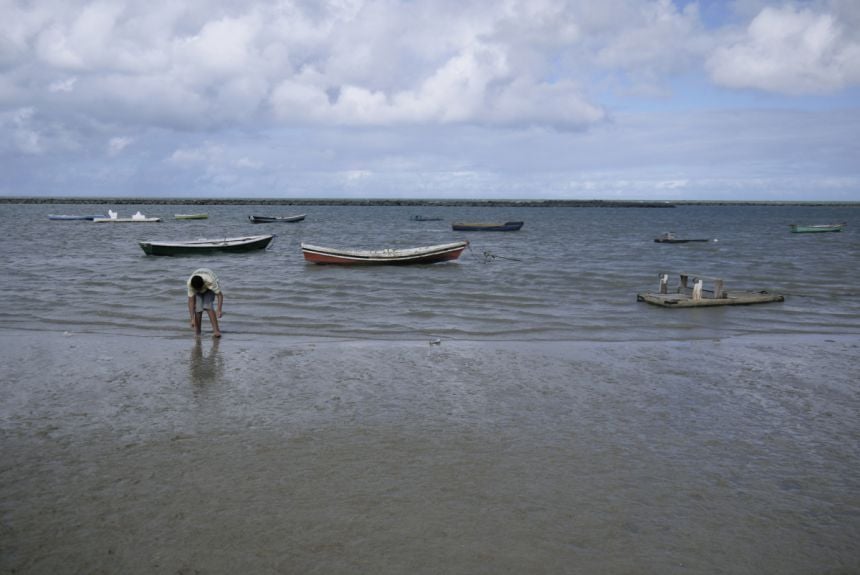 Credit: Lily Green
Credit: Lily Green'The students sometimes move to Brazil with certain preconceptions about the country, and it is always fascinating to see how their views and understanding of Brazilian culture change.
'It will be an opportunity for Brazilians to see themselves through young foreign eyes, and for the students to share what they learn during their time in the country – in terms of both language and culture.
'The BBC Brasil website is an amazing platform for the work of our future Brazilianists.'
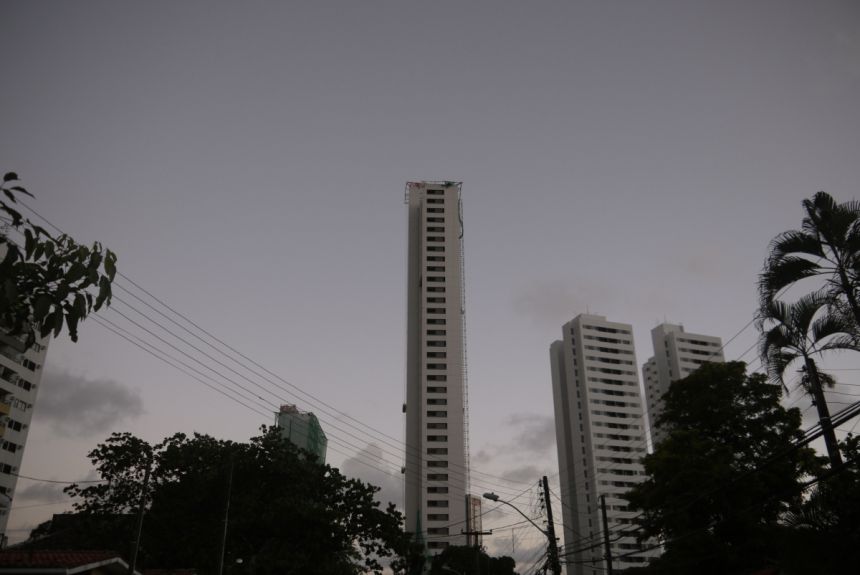 Credit: Lily Green
Credit: Lily GreenShe said: 'The title is so perfect, really. To get a sense of what it really meant, I would ask people I met what the phrase meant to them. Many people hadn't heard it before but for most it was something false, or something put on just for show.
'In my head I find it easiest to understand it as "sweeping things under the carpet" – not just because you don't want to deal with a problem, but because you don't want anyone to see there is a problem at all.
'So in the first post I was trying to get my head round the title but also highlight a few things I had spied under the metaphorical rug of sunny Brazil – the way there are always two sides to the coin in every aspect of the country. For example, luxury new-age shopping centres sit side-by-side with interior country landscapes that remind me of Nepal; breathtaking natural beauty is coupled with really shocking industrial pollution.'
 Credit: Lily Green
Credit: Lily Green'The Oxford University students taking part in this project are assuming the role of modern travellers who set out to explore Brazil, but instead of explaining it to their fellow countrymen they are talking to a Brazilian audience.
'We hope that this will be a two-way process in which Brazilians can learn from these students' perspectives and perhaps see how they themselves can contribute to a more diverse understanding of their own country.'
 Credit: Lily Green
Credit: Lily GreenWhen you think about evolution, 'survival of the fittest' is probably one of the first things that comes into your head. However, new research from Oxford University finds that the 'fittest' may never arrive in the first place and so aren’t around to survive.
By modelling populations over long timescales, the study showed that the 'fitness' of their traits was not the most important determinant of success. Instead, the most genetically available mutations dominated the changes in traits. The researchers found that the 'fittest' simply did not have time to be found, or to fix in the population over evolutionary timescales.
The findings suggest that life on Earth today may not have come about by 'survival of the fittest', but rather by the 'arrival of the frequent'. The study is published in the journal PLOS ONE and was funded by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council.
I caught up with the study's lead author Dr Ard Louis, Reader in Theoretical Physics at Oxford University, to find out more.
OxSciBlog: How do your results challenge current popular theory?
Ard Louis: We are arguing that some biological traits may be found in nature not because they are fitter than other potential traits but simply because they are easier to find by evolution. Darwinian evolution proceeds in two steps. Firstly, there is variation: due to mutations, different members of a population may have differences in traits. Secondly, there is selection: if the variation in a trait allows an organism to have more viable offspring, to be 'fitter', then that trait will eventually come to dominate in the population. Traditional evolutionary theory focuses primarily on the work of natural selection. We are challenging this emphasis by claiming that strong biases in the rates at which traits can arrive through variation may direct evolution towards outcomes that are not simply the 'fittest'.
OSB: What can mathematical models tell us about biological processes?
AL: Evolution is perhaps the field of biology where mathematics has been the most successful. For example, it was mathematically trained biologists like R. Fisher, J.B.S. Haldane and S. Wright who first worked out how to combine Mendelian genetics, which Darwin didn’t know about, with Darwinian evolution. Today, very sophisticated population genetic calculations are routinely used, for example, to work out how cancer evolves in a patient’s body.
Of course one always needs to be careful because these models inevitably include simplifying assumptions in order to make them tractable. In our calculations we include difference in rates of the arrival of variation, something not traditionally taken into account in population genetics. But our models so far only apply to fairly simple examples of molecular evolution. Much more work is needed before we could claim that these effects are also important for more complex phenomena such as the evolution of animal behaviour.
OSB: How do your calculations match up with real-world observations?
AL: We predict, for example, that RNA molecules that are more robust to the effect of mutations should naturally arise from our 'arrival of the frequent' effect. RNA can act both as an information carrier and as a catalyst, and so is thought to be very important for the origin of life on earth. It has been known for some time that RNA found in nature is remarkably robust to mutations and we can now provide a population genetic explanation of this phenomenon.
OSB: How have field biologists reacted to these results?
AL: On the one hand, biologists who work on evolution and development have not been so surprised because they have long argued that developmental processes can bias organisms to evolve in certain directions over others. Others have reacted with some caution, which is probably wise given the potentially far-reaching nature of our claims. I think we have raised a lot more questions that we have answered.
OSB: Did the results come as a surprise to you?
AL: On the one hand they didn't, in part because I have long been interested in Monte Carlo simulation techniques which have many parallels to evolution. There, biases in the arrival of variation are well known to affect outcomes. But I was very surprised to find that the biasing effect could be so enormously strong, making it robust to such a wide range of different evolutionary parameters.
OSB: How did your group come to study evolution?
AL: We specialise in statistical physics, and there are many beautiful parallels between evolutionary dynamics and processes in the everyday physical world. In my group we have worked for many years on self-assembly; how individual units can form well-defined composite objects without any external control. Biology is full of amazing self-assembled structures, and so we began asking: how do these structures evolve in the first place?
With the Golden Globes handed out and the Oscars looming, much of the media's attention is focused on the top films of the past 12 months.
Chief among them is Steve McQueen's 12 Years a Slave, which has already scooped the Golden Globe for Best Motion Picture amid a slew of other nominations and is the hot favourite to triumph at the Academy Awards in March.
The film, starring Chiwetel Ejiofor, Michael Fassbender, Lupita Nyong'o and Benedict Cumberbatch, is an adaptation of an 1853 memoir by Solomon Northup, a free-born African American from New York who was kidnapped by slave traders.
To coincide with the release of 12 Years a Slave, a BBC Culture Show special, presented by Mark Kermode, looked at the history and culture of slavery.
Oxford academic Jay Sexton, Deputy Director of the Rothermere American Institute (RAI), was one of the experts interviewed for the programme.
He said: 'To be a free black in the northern states would be much better than being a slave in the south, but there would be all sorts of limitations – both legal and political.'
Also interviewed was Richard Blackett of Vanderbilt University, Harmsworth Visiting Professor of American History at the RAI.
He said: 'Kidnapping was a major issue in mid 19th-century America. One can't quantify how many people were kidnapped, but a considerable number of free black people were kidnapped and sold into slavery.'
The programme can be viewed on BBC iPlayer here (link available until 12:04am, Saturday 1 February).
Leading figures from the arts, science and public policy came together in Oxford last night to discuss the value of the humanities in the 21st century.
Around 450 people packed into the University's Examination Schools to hear the views of, among others, Guardian chief arts writer Charlotte Higgins and Oxford mathematician Professor Marcus du Sautoy.
The event, which included a keynote speech from Dr Earl Lewis, President of the Andrew W. Mellon Foundation, kicked off the Humanities and the Public Good series, organised by The Oxford Research Centre in the Humanities (TORCH).
Among the audience given a warm welcome by the University's Vice-Chancellor, Professor Andrew Hamilton, were a number of school groups from across the UK.
Dr Lewis, in his speech titled 'In Everyone’s Interests: What it Means to Invest in the Humanities', said: 'Three quarters of a century ago, Virginia Woolf posed the question: if you had just three guineas to share, what would you support? In each age we face ostensibly insurmountable challenges that require choices to be made, resources to be allocated and areas to be ignored.
'The American Academy of Arts and Sciences argued in a recent report that we live in a world characterised by change, and therefore a world dependent on the humanities and social sciences.'
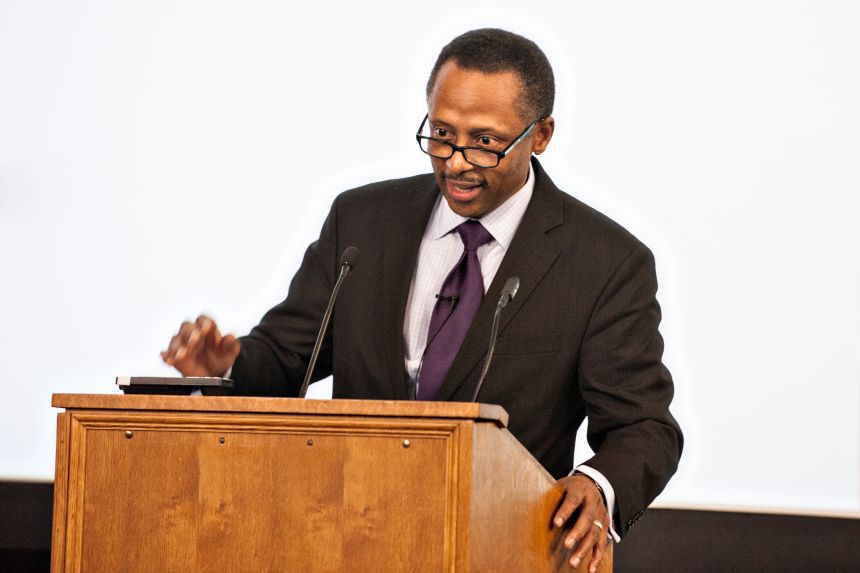 Dr Earl Lewis gave the keynote speech
Dr Earl Lewis gave the keynote speechHe added: 'We have to consider that the humanities continue to demonstrate the vibrant and dynamic tension between continuity and change. Longstanding disciplines such as literature, history and philosophy remain important to scholarship and discovery. And for nearly a quarter of a century we have also been embracing interdisciplinary scholarship.
'The humanities give us a fuller understanding of our world – past, present and future. The use of one's precious guineas in support of the humanities must start with a clear sense of its narrative, backed up by data. Investment then follows because the case for support is clear. That is why it is in everyone's interests to support the humanities and the public good – doing so advances our shared future.'
Responding to Dr Lewis's speech, Dame Hermione Lee, President of Wolfson College, Oxford, argued that those defending the humanities should not do so in an 'indignant, embattled or sentimental way'. She added: 'Why should we invest in the humanities? Because we're human.'
Charlotte Higgins, herself an Oxford classics graduate, called for the humanities not to be measured by the same criteria as the sciences, while Professor du Sautoy hailed the value of narrative, storytelling and collaboration in his own discipline.
Nick Hillman, Director of the Higher Education Policy Institute and a late addition to the panel, suggested that humanities scholars need to become better at engaging with policy makers, adding that the humanities have an unfortunate tendency to fight the previous battle rather than the current one.
And in an audience question and answer session chaired by Professor Shearer West, Head of the Humanities Division at Oxford, topics covered included why a sixth former should study a humanities subject at university; the value of longitudinal career studies into humanities graduates; the relationship between humanities study and employment prospects; and funding for the arts and humanities.
Information on the rest of the Humanities and the Public Good series can be found here.
Images: Stuart Bebb (stuartbebb.com)
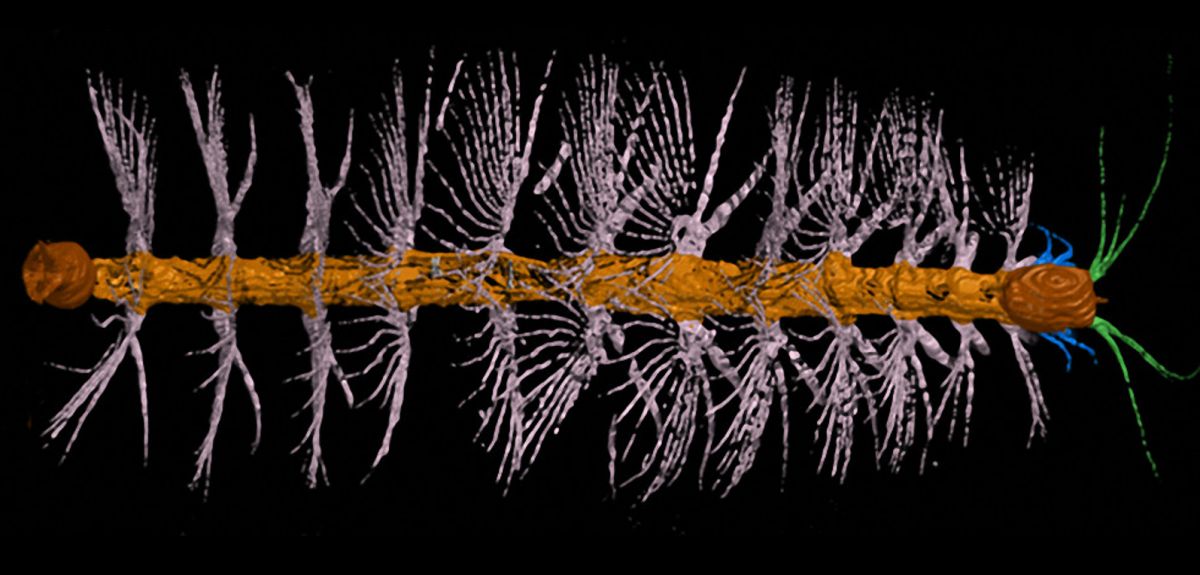
Palaeobiologists at Oxford University have discovered a new fossil arthropod, christened Enalikter aphson, in 425-million-year-old rocks in Herefordshire. It belongs to an extinct group of marine-dwelling 'short-great-appendage' arthropods, Megacheira, defined by their claw-like front limbs.
Arthropods are a highly diverse family of invertebrates that include insects, arachnids and crustaceans, making up some 85 percent of all described animal species. The discovery and analysis of Enalikter aphson has given support to the notion that Megacheira came before the last common ancestor of all living arthropods in the tree of life. If correct, this would indicate that megacheirans were distant ancestors of all arthropods alive today.
Enalikter was just 2.4 centimetres long with a rounded rectangular head, no eyes and a curved, whip-like feature protruding from in front of its mouth that may have been used in feeding – for example to capture smaller marine invertebrates.
At the rear end of its stick-like body there were two pincer-like projections that were attached to a primitive 'tail', and which may have been used for defence against predators. The extinct arthropod had no hard shell but is nevertheless remarkably well preserved in a hard nodule of minerals comprised mainly of calcite. Professor Derek Siveter, lead author of the study from the Oxford University Museum of Natural History and Department of Earth Sciences, said: 'Enalikter aphson had a soft and flexible body so it is incredible that it survived. The nodule acted like a womb and kept the creature free from decay and destruction, which would normally have happened very quickly. It meant it was able to survive all the earth movements and history that have happened since.'
The researchers were able to reconstruct the specimen in 3D thanks to its perfect preservation in the nodule. The nodule was investigated by optical tomography, a technique that can be used to create digital reconstructions of 3D objects using a series of finely-spaced images. To reconstruct Enalikter, the researchers imaged sequential surfaces of the fossil, spaced a mere 20 microns – thousandths of a millimetre – apart. These numerous images were then edited on a computer, in places pixel by pixel, to identify true biological structures from background 'noise'.
'In 3D it looks a bit like a tiny bottle brush, or even a Christmas tree. It is beautiful,' said Professor Siveter. 'It has provided us with exceptional data for the fossil record. Its soft body shell, or cuticle, is less than 10 microns thick. It was organic but has not decayed. That is amazing. Such exceptional preservation represents the jewel in the crown of palaeontology and provides so much more information than what does the typical shelly fossil record. It offers a rare window on the marine community back then.'
The newly-discovered animal, described in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B, lived so long ago that the UK would have been south of the Equator near where the Caribbean islands are now.
'It would have lived on the seabed in water possibly up to about 100 or 200 metres deep, at a time known as the Silurian, when invertebrates were just beginning to move onto land,' said Professor Siveter. 'It would have been a very warm, subtropical environment.'
The Herefordshire site where the fossil was discovered has been a real treasure trove for Professor Siveter and colleagues for almost twenty years, providing valuable clues about what life on Earth was like in ancient times.
- ‹ previous
- 175 of 252
- next ›



 Learning for peace: global governance education at Oxford
Learning for peace: global governance education at Oxford  What US intervention could mean for displaced Venezuelans
What US intervention could mean for displaced Venezuelans  10 years on: The Oxford learning centre making an impact
10 years on: The Oxford learning centre making an impact Oxford and The Brilliant Club: inspiring the next generation of scholars
Oxford and The Brilliant Club: inspiring the next generation of scholars New course launched for the next generation of creative translators
New course launched for the next generation of creative translators The art of translation – raising the profile of languages in schools
The art of translation – raising the profile of languages in schools  Tracking resistance: Mapping the spread of drug-resistant malaria
Tracking resistance: Mapping the spread of drug-resistant malaria