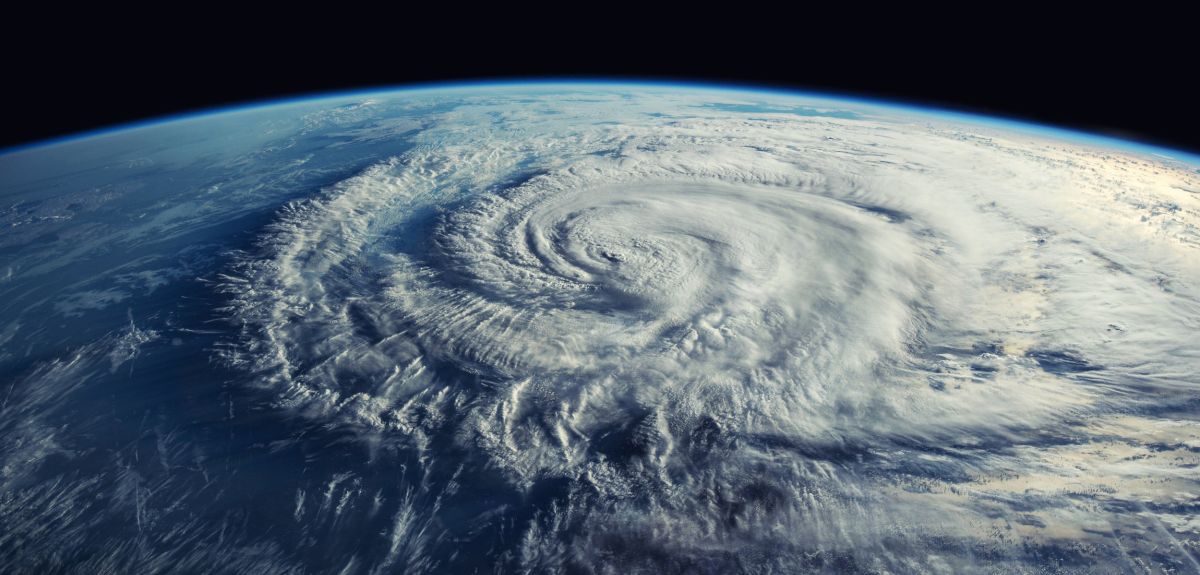

New algorithm supercharges climate models and could lead to better predictions of future climate change
Professor Samar Khatiwala, from the University of Oxford’s Department of Earth Sciences, has led a major advance to solve a critical issue in modelling future climate change. The findings have been published in Science Advances.
Minimising model drift at a much lower cost in time and energy is obviously critical for climate change simulations, but perhaps the greatest value of this research may ultimately be to policy makers who need to know how reliable climate projections are.
Study author Professor Samar Khatiwala, Department of Earth Sciences, University of Oxford
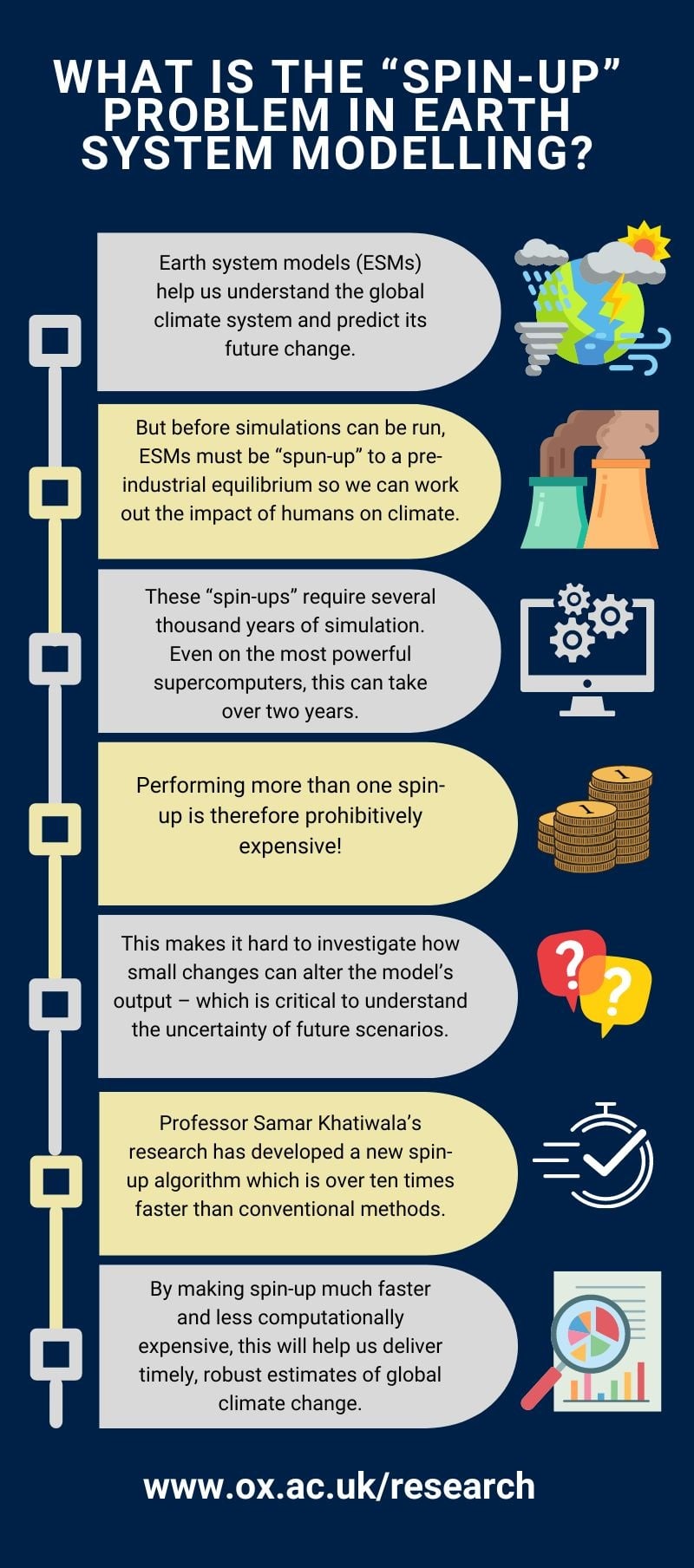
Earth System Models – complex computer models which describe Earth processes and how they interact – are critical for predicting future climate change. By simulating the response of our land, oceans, and atmosphere to manmade greenhouse gas emissions, these models form the foundation for predictions of future extreme weather and climate event scenarios, including those issued by the UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
However, climate modellers have long faced a major problem. Because Earth System Models integrate many complicated processes, they cannot immediately run a simulation; they must first ensure that it has reached a stable equilibrium representative of real-world conditions before the industrial revolution. Without this initial settling period – referred to as the “spin-up” phase – the model can “drift”, simulating changes that may be erroneously attributed to manmade factors.
Unfortunately, this process is extremely slow as it requires running the model for many thousands of model years which, for IPCC simulations, can take as much as two years on some of the world’s most powerful supercomputers.
Spin-up has always been prohibitively expensive in terms of computational cost and time. The new approaches developed by Professor Khatiwala have the promise to break this logjam and deliver a quantum leap in the efficiency of spinning up such complex models and, as a consequence, greatly increase our ability to deliver timely, robust estimates of global climate change.
Professor Colin Jones Head of the NERC/Met Office sponsored UK Earth system modelling, commenting on the findings
However, a new study published in Science Advances by a University of Oxford scientist funded through the Agile Initiative describes a new computer algorithm which can be applied to Earth System Models to drastically reduce spin-up time. During tests on models used in IPCC simulations, the algorithm was on average 10 times faster at spinning up the model than currently-used approaches, reducing the time taken to achieve equilibrium from many months to under a week.
Study author Samar Khatiwala, Professor of Earth Sciences at the University of Oxford’s Department of Earth Sciences, who devised the algorithm, said: ‘Minimising model drift at a much lower cost in time and energy is obviously critical for climate change simulations, but perhaps the greatest value of this research may ultimately be to policy makers who need to know how reliable climate projections are.’
Currently, the lengthy spin-up time of many IPCC models prevents climate researchers from running their model at a higher resolution and defining uncertainty through carrying out repeat simulations. By drastically reducing the spin-up time, the new algorithm will enable researchers to investigate how subtle changes to the model parameters can alter the output – which is critical for defining the uncertainty of future emission scenarios.
Policymakers rely on climate projections to inform negotiations as the world tries to meet the Paris Agreement. This work is a step towards reducing the time it takes to produce those critical climate projections.
Professor Helene Hewitt OBE, Co-chair for the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project (CMIP) Panel, which will inform the next IPCC report, commenting on the findings
Professor Khatiwala’s new algorithm employs a mathematical approach known as sequence acceleration, which has its roots with the famous mathematician Euler. In the 1960s this idea was applied by D. G. Anderson to speed-up the solution of Schrödinger’s equation, which predicts how matter behaves at the microscopic level. So important is this problem that more than half the world’s supercomputing power is currently devoted to solving it, and ‘Anderson Acceleration’, as it is now known, is one of the most commonly used algorithms employed for it.
Professor Khatiwala realised that Anderson Acceleration might also be able to reduce model spin-up time since both problems are of an iterative nature: an output is generated and then fed back into the model many times over. By retaining previous outputs and combining them into a single input using Anderson’s scheme, the final solution is achieved much more quickly.
Not only does this make the spin-up process much faster and less computationally expensive, but the concept can be applied to the huge variety of different models that are used to investigate, and inform policy on, issues ranging from ocean acidification to biodiversity loss. With research groups around the world beginning to spin-up their models for the next IPCC report, due in 2029, Professor Khatiwala is working with a number of them, including the UK Met Office, to trial his approach and software in their models.
The study ‘Efficient spin-up of Earth System Models using sequence acceleration’ has been published in the journal Science Advances.
 Expert Comment: Four years of full-scale war and Ukrainian resistance continues
Expert Comment: Four years of full-scale war and Ukrainian resistance continues
 Oxford and Liverpool join forces to tackle global challenges
Oxford and Liverpool join forces to tackle global challenges
 Chancellor of Oxford University hosts special honorary degree ceremony
Chancellor of Oxford University hosts special honorary degree ceremony
 Extremely hot days are warming twice as fast as average summer days in North-West Europe
Extremely hot days are warming twice as fast as average summer days in North-West Europe
 Oxford climate scientists: No doubt about climate change.
Oxford climate scientists: No doubt about climate change.
 Climate concern: Extreme heat going unrecorded in Africa
Climate concern: Extreme heat going unrecorded in Africa