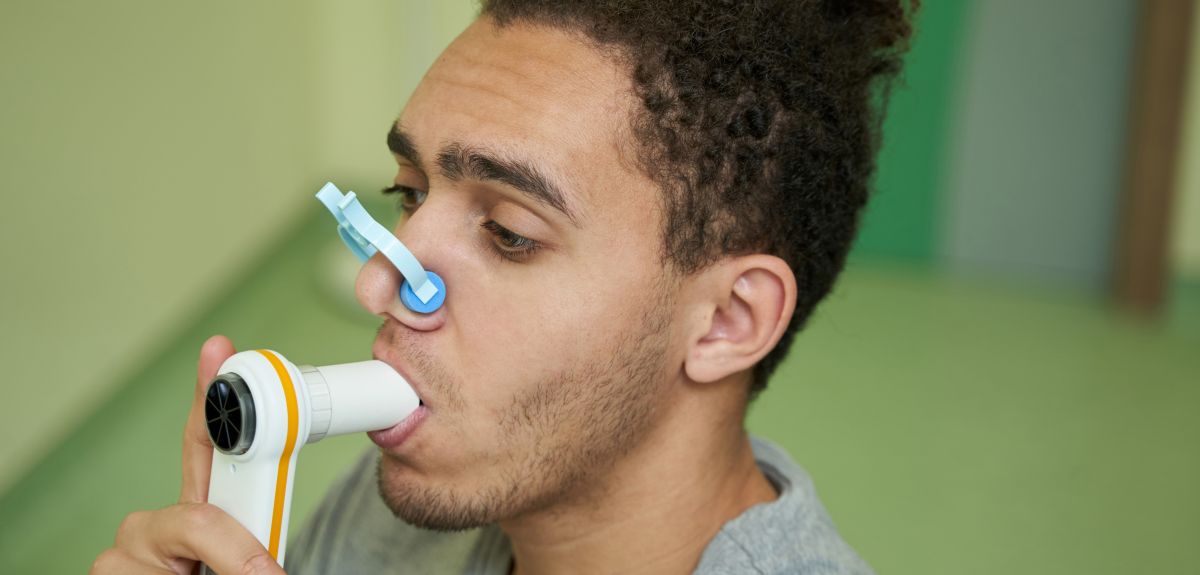
Novel inhaled TB vaccine
The Jenner Institute is conducting a new study, using BCG, the current licensed vaccine against tuberculosis. In this study, they will give BCG a second time to people who have already had BCG once before, and will compare whether giving it by inhalation is better at protecting people against tuberculosis than giving it into the skin
As the natural route of infection with tuberculosis is through inhalation of droplets into the lungs, this study, which delivers BCG by the same route, is hoped to be better at stimulating the immune system.
Prof Helen McShane Chief Investigator, TB Vaccine Trials Jenner Institute, University of Oxford, said:
TB kills more people than any other infectious disease and we urgently need better vaccines. This important new study will help us to see whether giving BCG more than once stimulates a stronger immune response and whether giving it by inhalation is better than giving it into the skin. Small studies like these are really important to help us understand the immune response in people and allow us to design and test better vaccines.
This study will also explore whether giving people with Type 2 Diabetes BCG in the skin stimulates as strong an immune response as giving BCG in the skin to healthy people without diabetes. We know that people with type 2 diabetes are more likely to get TB and part of this may be because the BCG vaccine does not work as well in this group
This study will recruit healthy volunteers, with and without Type 2 Diabetes, who have previously been vaccinated with BCG. The volunteers will be split into 3 groups of 12 volunteers each. If eligible, volunteers will either receive BCG vaccine either as an injection in the skin or as an inhaled vaccine. All participants will be followed up for 6 months after receiving BCG with close monitoring for side effects and to evaluate the immune response.
About Tuberculosis and BCG (Bacille Calmette-Guérin)
TB is a disease caused by a bacterium known as Mycobacterium Tuberculosis and remains one of the top 10 causes of death worldwide, and the largest infectious killer. BCG given as a single dose under the skin, is the only vaccine currently licenced for use against TB, but it is not always protective. The BCG vaccine works well against disease in childhood, but it is not good enough at protecting against disease in adulthood, which is when the majority of TB deaths occur.
Aye Thu Clinical Research Fellow Centre for Clinical Vaccinology and Tropical Medicine, said: “Despite BCG vaccine being around for more than 100 years, Tuberculosis remains the leading cause of death from an infective cause. A significant proportion of the population infected with TB continue to get sick and die even with TB medication. Having a new way of optimizing the BCG vaccine will ultimately improve the health of people all over the world. This study will give the participants an opportunity to get involved in testing an exciting new way of delivering BCG vaccine through the aerosol route.”
Further information:
Further information and contact details
Thank you for your interest in the trial, we hope this information sheet has answered all of your questions. If you would like further information about taking part in research please visit the following website: [http://www.nhs.uk/conditions/clinical-trials/pages/introduction.aspx].
For independent advice about taking part in this study, you may wish to contact your GP. If you would like to speak to one of our study doctors or Professor Helen McShane (Chief Investigator) to discuss any aspect of this study, or if you would like to take part in this study, please contact:
Volunteer Recruitment Coordinator
Centre for Clinical Vaccinology & Tropical Medicine
Churchill Hospital, Old Road, Headington, Oxford, OX3 7LE
Telephone: 01865 611424
Email: [email protected]
 British children are growing taller but not for the right reasons
British children are growing taller but not for the right reasons
 Expert Comment: The war in the Gulf
Expert Comment: The war in the Gulf
 International Advisory Board to strengthen global leadership in primary care
International Advisory Board to strengthen global leadership in primary care
 Expert Comment: Church-to-mosque conversions grab headlines, but is funding the real crisis?
Expert Comment: Church-to-mosque conversions grab headlines, but is funding the real crisis?