White dwarf star discovered emitting rapid gas flares for the first time
Incredibly rapid gas flares have been detected coming from a white dwarf binary star system for the first time by Oxford University scientists. The first sighting of such activity, it suggests that our current understanding of star habits and their capabilities is incomplete.
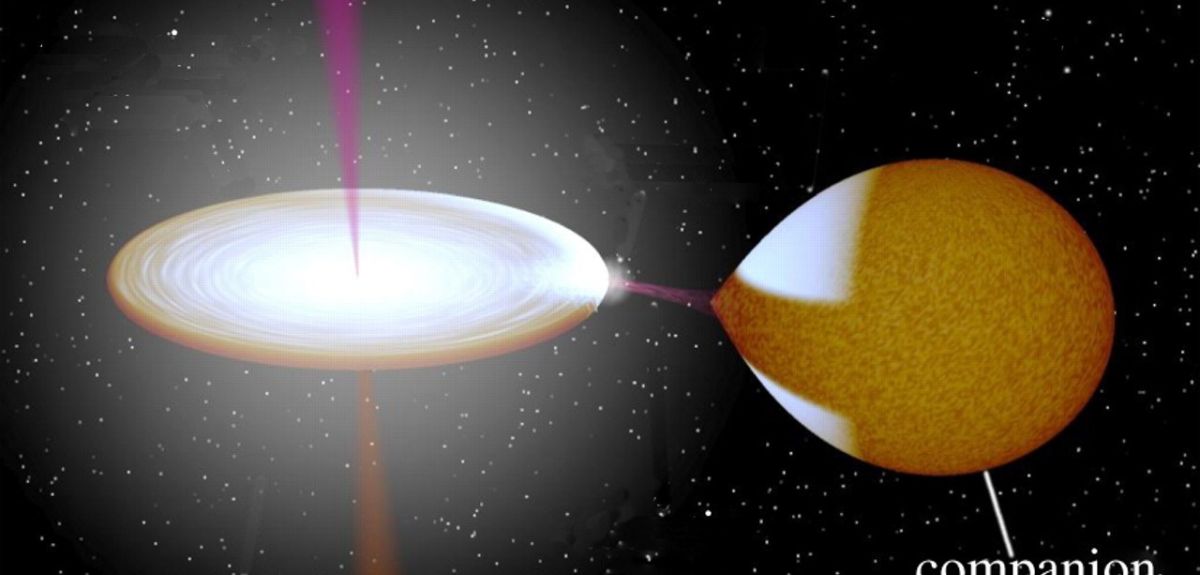
Dwarf novae (objects which contain a Sun-like star orbiting a white dwarf star) are well known for their repeated, low-level, bursting behaviour (called "outbursts") but they have never been observed exhibiting behaviour on anything like the scale of rapid flares before.
Outbursts have previously been seen in white dwarfs, neutron stars and even enormous black holes residing in different galaxies. Such stars mainly feed on gas from their companion stars via accretion (where a large amount of gas is accumulated and builds up through gravitational force). Occasionally, these stars "throw up" some of the gas in the form of jets, which are powerful overflows of gas restricted to a single, narrow, cone-like flow.
We expected to see slow variation flares, but found fast, rapid, cone-like spikes of activity and observed an enormous amount of energy being released in a time-span as short as ten minutes. Nothing like this has ever been seen before in a dwarf nova system.
Dr. Kunal Mooley, Astrophysics research fellow
Initial observations of the dwarf novae, SS Cyg, activity in February 2016 were considered an atypical outburst, but later telescopic analysis uncovered the intriguing revelation of rapid flares. The most fascinating and unexpected behaviour was observed at radio wavelengths towards the end of the outburst, when a “giant” flare was observed. Lasting for less than 15 minutes, it had the energy of more than a million times the strongest solar flares. The level of radio data recorded from the flare is unprecedented in dwarf nova systems and consistent with that expected from a jet.
Dr. Kunal Mooley, Astrophysics research fellow at Oxford University, who led the research, said: “Many of astrophysics’ most compelling studies have been based on studying SS Cyg. The latest, a detection of a rapid, radio flare – especially a fast, bright flare towards the end of the outburst, is highly unusual and demonstrates that there may even be some new physics at play. We expected to see slow variation flares, but found fast, rapid, cone-like spikes of activity and observed an enormous amount of energy being released in a time-span as short as ten minutes. Nothing like this has ever been seen before in a dwarf nova system.
“Moving forward, theorists should work with observers to find the answer to why these rapid flares occurred in SS Cyg. To really understand the process of gas accretion and gas expulsion in white dwarf systems – especially dwarf novae, similar studies should be carried out on other astrophysical systems.”
First discovered over one hundred years ago, SS Cyg has been studied extensively by astronomers. The star continues to provide new insights into the physical processes associated with white dwarf binary systems, such as those found by Dr Mooley’s team.
Dr Mooley and his team at Oxford are now conducting further analyses, and working to build a body of conclusive events about dwarf nova behaviours and establish if they are in fact capable of launching powerful jets.
Full findings were published in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society
mnrasl.oxfordjournals.org/content/early/2016/12/05/mnrasl.slw243.full.pdf+html
Findings are also available from Cornell University Library:https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.0706 4
 Expert Comment: Is an under-16 social media ban the right course?
Expert Comment: Is an under-16 social media ban the right course?
 ADHD medication use rises sharply across Europe, driven by growth among adults
ADHD medication use rises sharply across Europe, driven by growth among adults